How Marijuana Affects Your Body


It Makes You High
Let’s be honest: This is why most people use marijuana. THC is what causes the high. When you smoke marijuana, THC goes from your lungs to your bloodstream and then makes its way to your brain. There it connects to parts of certain cells called receptors. That’s what gives you those pleasant feelings. You can also get marijuana in things like cookies, gummies, and brownies. These are called edibles. They get into your blood through your digestive system.

Brain
You might find it harder to focus, learn, and remember things when you use marijuana. This short-term effect can last up to 24 hours after you stop smoking. Long-term use, especially in your teens, may have more permanent effects. Imaging tests that take pictures of the brain show fewer connections in areas linked to alertness, learning, and memory. Tests show lower IQ scores in some people.

Lungs
Marijuana smoke can inflame your lungs. If you’re a regular user, you could have the same breathing problems as a cigarette smoker. That means a cough, sometimes long lasting, or chronic. It might produce colored mucus, or phlegm. You could also be more likely to get lung infections. Inflamed lung tissue is part of the reason, but THC also seems to affect the way some people’s immune systems work.
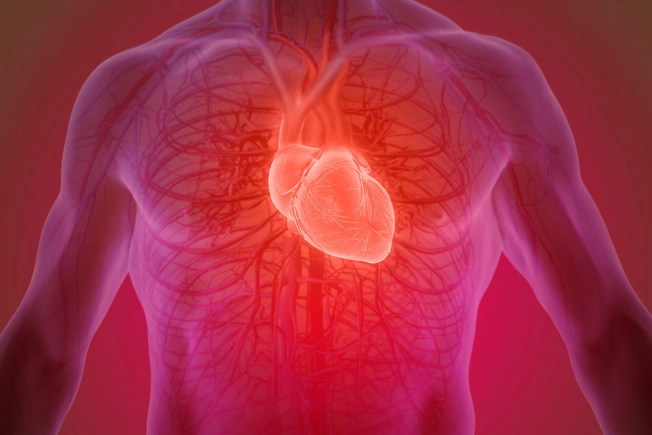
Heart
Your normal heart rate of 50 to 70 beats per minute can rise by 20 to 50 beats or more for up to 3 hours after you use marijuana. Scientists think that this, along with tar and other chemicals in the drug, may raise your chance of a heart attack or stroke. The risk could go up further if you’re older or you already have heart problems.

Mental Health
Anxiety and paranoia are common complaints among marijuana users. Clinical anxiety and depression are also more likely, but scientists aren’t yet sure exactly why. The drug can make symptoms of more serious mental illness like psychosis and schizophrenia worse. It’s also linked to a higher likelihood of substance abuse. These effects could be worse if your genes make you more likely to get a mental illness or an addiction.

Appetite
Regular marijuana users often refer to this as the munchies. Some reports suggest this increased appetite might help you gain weight lost to illnesses like AIDS or cancer, or because of treatment for those diseases. Scientists are still studying when and if the treatment works or if it’s safe.
Stomach
By itself, THC (marijuana’s active ingredient) seems to ease nausea, especially if your symptoms are from chemotherapy treatment for cancer. Some people say the stomach-settling effects work better when you use marijuana instead of THC alone. This may be because other chemicals enhance the effects of THC. But long-term marijuana use can have the opposite effect and cause more vomiting. Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome can occur in regular users and leads to frequent vomiting.
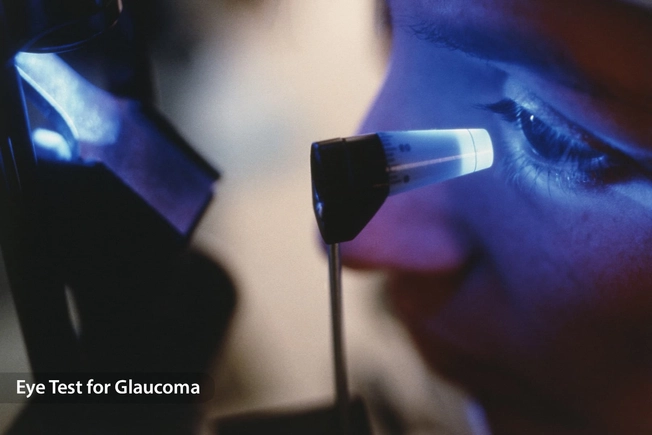
Eyes
Some evidence suggests that marijuana, or chemicals in it, can lower the eye pressure that’s a main symptom of glaucoma. The problem is the effect only lasts 3 to 4 hours. To keep it low, you’d have to get the drug into your bloodstream 6-8 times a day. Doctors have yet to come up with a form of the drug that’s safe to use as a glaucoma treatment. And though marijuana does seem to lower eye pressure, it also might reduce the blood supply to your eye, which could make glaucoma worse.
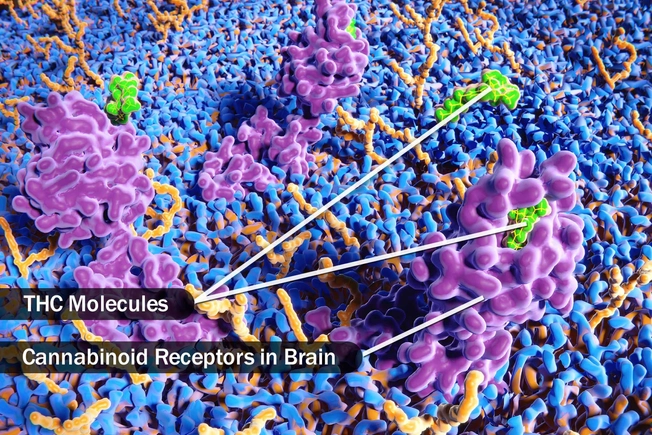
Chronic Pain
Both marijuana and a pill version of THC called dronabinol seem to help relieve pain by attaching to parts of brain cells called cannabinoid receptors. Some studies suggest CBD oil could ease pain from arthritis, nerve damage (neuropathy), and muscle spasms, among other causes. Scientists continue to study how and when and if this works in people.
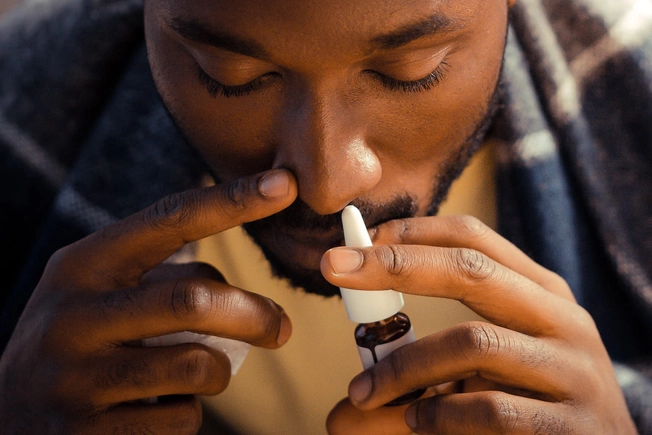

Multiple Sclerosis
A version of THC that you spray up your nose called nabiximols is available in Canada, the U.K., and other countries. It seems to help calm muscle spasms, lessen nerve pain, and improve sleep for many people with multiple sclerosis. It may also help with other illnesses, like cancer. The FDA is working to test the drug for use in the U.S.

Inflammation
Though smoking marijuana can inflame your lungs, substances called cannabinoids seem to lessen the swelling in certain other tissues. Cannabidiol may be a good choice because it doesn’t cause the same high as THC. In animal tests, it shows some promise in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and conditions that inflame the digestive tract, like ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
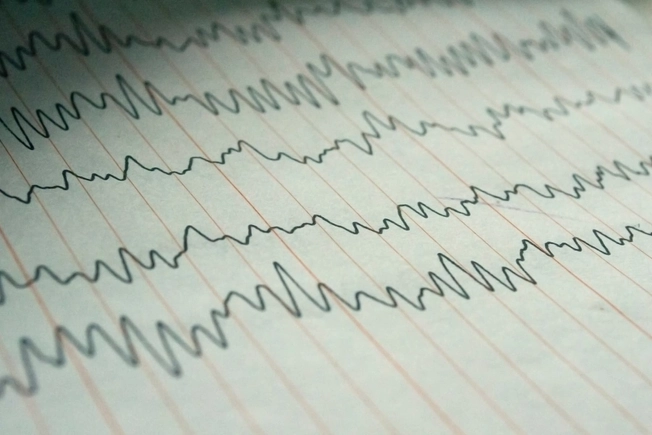

Seizures
There’s good evidence that marijuana, or drugs made from it, may help lessen seizures in some people with epilepsy. The FDA has even approved a drug made with cannabidiol for that purpose (Epidiolex). But the agency only recommends it for two rare forms of childhood epilepsy called Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
1) Science Source
2) Getty
3) Getty
4) Getty
5) Getty
6) Getty
7) Getty
8) Getty
9) Getty
10) Getty
11) Getty
12) Getty
SOURCES:
British National Health Service: “Cannabis: the facts.”
CDC: “Marijuana and Public Health.”
Colorado Department of Public Health: “FAQ -- Health Effects of Marijuana.”
Epilepsy Currents: “Cannabidiol: Promise and Pitfalls.”
European Journal of Pain: “Transdermal cannabidiol reduces inflammation and pain-related behaviours in a rat model of arthritis.”
Glaucoma Research Foundation: “Should You Be Smoking Marijuana To Treat Your Glaucoma?”
Government of Canada Department of Public Health: “Health effects of cannabis.”
Journal of Epilepsy Research: “Cannabinoids in the Treatment of Epilepsy: Hard Evidence at Last?”
Journal of Experimental Medicine: “Cannabinoids suppress inflammatory and neuropathic pain by targeting α3 glycine receptors.”
National Cancer Institute: “Cannabis and Cannabinoids (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version.”
National Institute on Drug Abuse: “Marijuana,” “What are marijuana's effects on lung health?”
“What are marijuana's long-term effects on the brain?” “What is marijuana?”
Nemours Foundation: “Marijuana.”
New England Journal of Medicine: “Adverse Health Effects of Marijuana Use.”
FDA: “FDA approves first drug comprised of an active ingredient derived from marijuana to treat rare, severe forms of epilepsy.”